|
HLIBpro
2.5.1
|
The following parameters of 𝖧𝖫𝖨𝖡𝗉𝗋𝗈 are defined in the HLIB::CFG namespace with corresponding sub namespaces.
You may either read/write the parameters within your source code, e.g.,
or via environment variables. In the latter case, "::" is replaced by "_" and "CFG" is omitted, e.g., instead of HLIB::CFG::BLAS::use_rrqr_trunc the environment variable HLIB_BLAS_use_rrqr_trunc is used with boolean values defined by 0 or 1.
Furthermore, a list of all parameters with values may be printed via
In the C bindings the corresponding functions for setting, reading and printing the parameters are
Please note, that the names and values correspond to the names and values of the environment variables and not of the C++ parameters.
| Name | Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
use_rrqr_trunc | bool | use RRQR based truncate instead of SVD based | false |
use_double_prec | bool | use double precision SVD for single precision types | false |
use_gesvj | bool | use gesvj instead of gesvd/gesdd | false |
gesvd_limit | idx_t | upper matrix size limit for using *gesvd (*gesdd for larger matrices) | 1000 |
check_zeroes | bool | check for and remove zero rows/columns in input matrices of SVD | false |
check_inf_nan | bool | check for INF/NAN values in input data | false |
Rank-revealing QR (RRQR) uses column pivoted QR to determine the numerical rank of a given matrix. This is used in 𝖧𝖫𝖨𝖡𝗉𝗋𝗈 to truncated low-rank matrices with respect to a given precision or rank. In contrast to the SVD based algorithm, RRQR does usually not compute a best approximate, which normally results in a larger rank of the low-rank matrices or reduced accuracy in case of a fixed rank. However, the RRQR algorithm is faster than SVD, which results in a better runtime of the ℋ-algorithm.
Please note, that this behaviour is strongly depended on the given ℋ-matrix. In extreme cases, the ℋ-arithmetic may be slower since the rank of low-rank matrices may be much higher compared to SVD.
If 𝖧𝖫𝖨𝖡𝗉𝗋𝗈 is compiled with single precision value types, setting use_double_prec to true, results in using double precision for computing the SVD during truncation. This increases accuracy and may reduce memory due to more accurate rank estimates.
LAPACK provides an additional SVD algorithm (gesvj), which is often more accurate compared to the standard algorithms (gesvd, gesdd). Especially for extreme cases, e.g., very small singular values, this may be a better choice. However, gesvj is slower compared to the other algorithms (usually a factor of two).
The SVD based algorithm may have problems of the input matrix has zero rows/columns (more precise the LAPACK algorithms used by the truncation). To fix this, such rows/columns can be eliminated from the input matrices.
| Name | Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
nmin | uint | upper limit for minimal block size | 60 |
split_mode | default split mode during geometrical clusterung | adaptive_split_axis | |
adjust_bbox | bool | adjust bounding box during clustering to local indices and not as defined by parent partitioning | true |
cluster_level_mode | permit block clusters with clusters from different levels or not | cluster_level_equal | |
sync_interface_depth | bool | synchronise depth of interface clusters with domain clusters in ND case | true |
sort_wrt_size | bool | sort sub clusters according to size, e.g. larger clusters first | false |
The optimal value for nmin depends on the given problem and what is to be optimised: memory or runtime. As a rule of thumb, the smaller nmin the less memory is used and the larger nmin the better the runtime.
The default value is chosen based on benchmarks for dense matrices. For sparse matrices a higher value is often better (nmin = 100 ... 300).
When partitioning a given geometry using binary space partitioning (BSP), the split axis may be chosen regularly (regular_split_axis), i.e., cycling through x, y and z axis or adpative (adaptive_split_axis), i.e., choose the longest axis. Theory usually assumes regular splitting while adaptive splitting often results in a better (less memory, better runtime) partitioning.
During BSP the sub domains may be assigned a bounding box by splitting the bounding box of the parent domain along the split axis or by recomputing the bounding box based on the coordinate information of the indices in the corresponding sub domains. The latter method usually reduces bounding box sizes and leads to a coarser partitioning of the ℋ-matrix, which in practise is often more optimal (less memory, better runtime). However, theory usually assumes a non-adaptive bounding box.
When building block clusters, i.e., a product of two clusters, normally only clusters of the same level are permitted to form block clusters. For some applications it may result in a better partitioning when also allowing clusters from different levels during block cluster tree construction (see also sync_interface_depth).
If nested dissection is used, the depth of the interface tree is normally adjusted to the depth of the domain trees. For some applications, switching this off may result in a better partitioning (see also cluster_level_mode).
| Name | Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
use_dag | bool | use DAG based arithmetic | true |
abs_eps | real | default absolute error bound for low-rank SVD | 0 |
recompress | bool | recompress matrix after low-rank approximation | true |
use_zero_matrix | bool | use special zero matrix type for domain-domain blocks | true |
build_ghost_matrix | bool | build ghost matrices for remote blocks | false |
build_sparse_matrix | bool | use sparse matrices during construction | false |
eval_type | point-wise or block-wise evaluation of blocks | block_wise | |
storage_type | storage type of diagonal blocks in factorisation | store_inverse | |
max_seq_size | size_t | switching point from parallel to sequential mode | 100 |
max_seq_size_vec | size_t | switching point for vector based operations | 250 |
coarsen_build | bool | coarsen matrix during construction | false |
coarsen_arith | bool | coarsen matrix during arithmetic | false |
check_cb_ret | bool | check data returned by callback functions during construction | true |
arith_max_check | uint | upper matrix size limit for addition tests during arithmetic | 0 |
For multi and many core chips, the DAG based ℋ-arithmetic is able to utilise the CPU resources much better than the classical recursive algorithms. Only for sequential computations, a slightly better runtime may be possible with the recursive approach due to overhead for DAG based computations.
Singular values smaller than abs_eps are removed from the resulting matrix during truncation independent on the given accuracy or rank.
The low-rank approximations computed during ℋ-matrix construction may not be optimal with respect to the rank. A recompression using SVD (or RRQR) may reduce the rank and hence memorr without affecting accuracy.
When using nested dissection, off-diagonal domain-domain blocks remain zero during ℋ-LU factorisation. A special matrix type can therefore be used to signal this property to the ℋ-arithmetic and to improve performance of the algorithms.
However, make sure that only such ℋ-algorithms are used, which preserve the zero property. Otherwise, an error may occur.
The evaluation type affects the handling of diagonal leaf blocks. Either factorisation is also performed for such blocks (point_wise) or the blocks are handled as a full block using inversion (block_wise). The latter has several advantages, e.g., permits limited pivoting during inversion and increases performance due to better cache utilisation (BLAS level 3 functions).
When computing matrix factorisations, the diagonal leaf blocks may store either the actual result of the factorisation (store_normal) or the inverse of such blocks (store_inverse). Since for evaluation of the inverse operators, either during factorisation or during matrix-vector multiplication, the inverse if the matrix blocks is needed, storing the inverse results in better performance.
However, if also the original matrix should be evaluated using the factorised form, normal storage may be more optimal in terms of runtime.
Matrices smaller than max_seq_size are handled by ℋ-arithmetic sequentially since this is more efficient compared to parallel handling. Same holds for max_seq_size_vec in case of matrix-vector operations.
| Name | Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
max_iter | uint | maximal number of iterations | 100 |
rel_res_red | real | relative residual reduction, e.g., stop if 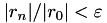 | 1e-8 |
abs_res_red | real | absolute residual reduction, e.g., stop if 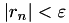 | 1e-14 |
rel_res_growth | real | relative residual growth (divergence), e.g., stop if 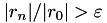 | 1e6 |
gmres_restart | uint | restart for GMRES iteration | 20 |
initialise_start_value | bool | initialise start value before iteration | true |
use_exact_residual | bool | compute exact residual during iteration | false |
This parameter stops the iteration in case of divergence.
Normally, the start value of the iteration is initialised as 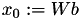 with
with 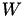 being the preconditioner. In case of a good (or very good) preconditioner, e.g.,
being the preconditioner. In case of a good (or very good) preconditioner, e.g., 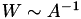 , this may eliminate iteration at all.
, this may eliminate iteration at all.
However, if the user has a good guess for the start value this behaviour may be switched off.
Most iterations approximate the residual norm during computations. Especially in the preconditioned case, this may result in a large deviation from the real residual norm. At the expense of one (unpreconditioned case) or two (preconditioned case) additional matrix-vector multiplications, the exact norm is computed instead.
| Name | Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
quad_order | uint | default quadrature order | 4 |
adaptive_quad_order | bool | use distance adaptive quadrature order | true |
use_simd | bool | use special vector functions if available | true |
use_simd_sse3 | bool | use special SSE3 vector functions if available | true |
use_simd_avx | bool | use special AVX vector functions if available | true |
use_simd_avx2 | bool | use special AVX2 vector functions if available | true |
use_simd_mic | bool | use special MIC vector functions if available | true |
For the evaluation of the bilinear forms a quadrature rule is used for which the default order is defined with this parameter. For high accuracy ℋ-arithmetic, a higher order may be used, e.g., 5 or 6.
For far-field evaluation, the quadrature order may be reduced for normal bilinear forms, resulting in much reduced runtime.
All implemented bilinear forms have special implementations using SIMD instructions of the CPU. Normally, this results in a faster computation compared to compiler generated code. So, in most cases this flag is only needed for comparison or for debugging.
| Name | Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
use_matlab_syntax | bool | use Matlab syntax for printing complex numbers, vectors and stdio | off |
color_mode | use color in terminal output if supported | true | |
charset_mode | use ascii or unicode in normal terminal output | depends on terminal |